Guideline for Manual Call Point
January 7, 2026 1 Comment
| MANUAL CALL POINT REFERENCE | |||
| Area | Code | Clause No | Descriptions |
| Mounting Height | NFPA 72 | 17.14.5 | The operable part must be between 1.07 meter to 1.22 meter above the finished floor. |
| BS 5839-1:2025 | 20.2 | Typically mounted at 1.4 meters (0.2m above or 0.3m below) allowing placement between 1.1 meter and 1.6 meter. For disabled access, heights may be lowered to 0.9 meter to 1.2 meter. | |
| IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | Call points shall be fixed at a height of 1.4 meter above the surrounding floor level, at easily accessible, we illuminated and conspicuous positions, which are free of obstructions. | |
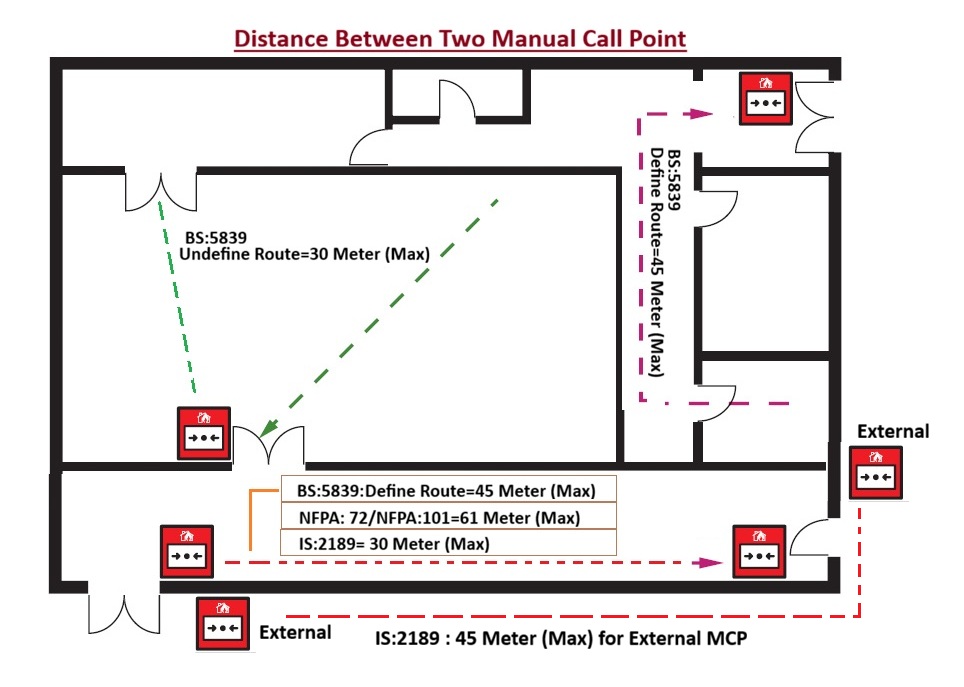
| From Door Distance | NFPA 72 | 17.15.9.6 | pull stations are required to be located within 1.5 meters of each exit doorway on every floor, ensuring they are easily reachable during emergencies. |
| NFPA 101 | 9.6.2.3 | the manual fire alarm box shall be located within 1525 mm of exit doorways. | |
| NFPA 101 | 9.6.2.4 | Manual fire alarm boxes shall be mounted on both sides of grouped openings over 40 ft (12.2 meter) in width, and within 1525 mm of each side of the opening. | |
| Travel Distance | NFPA 101 | 9.6.2.5 | No horizontal distance on that floor exceeding 200 ft (61 meter) shall need to be traversed to reach a manual fire alarm box. |
| BS 5839-1:2025 | 20.2 | MCPs must be on escape routes and Distribution of MCPs should be such that no one need travel more than 45 meter in certain route (or 30 meter if layouts are uncertain). For disabled residents this should be adapted to within 25 meter to 16 Meter of each other. For high-risk areas (e.g. kitchens or cellulose paint spraying) a MCP should be sited in close proximity. | |
| NFPA 72 | 17.15.9.5 | Additional manual fire alarm boxes shall be provided so that the travel distance to the nearest manual fire alarm box will not exceed 200 ft (61 meter), measured horizontally on the same floor. | |
| IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | Manual call points shall be so located that, to give an alarm, no person in the premises has to travel distance of more than 30 meter to reach them. When manual call points are also installed external to the building, the travel distance shall be 45 meter | |
| IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | Where necessary, the travel distance may require to be reduced to less than 30 meter, for example, where there is difficulty in free access within the risk or in potentially dangerous risks. | |
| Location | BS 5839-1:2025 | Not placing MCPs at non-final exits or in unsupervised areas like shopping centers. | |
| IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | Manual call point shall be located preferably near entry to staircases at various levels. | |
| NBC 2016 | J-9.1.4 | Manual call station(s) shall be provided at central location(s) on each platform (near emergency plunger) and at least two on the concourse, on each sidewall. When the concourse is in two halves, at least one manual call station shall be provided on each side. | |
| BS 5839-1:2017 | 20.2 | MCPs should be located on escape routes and, in particular, at all story exits and all exits to open air that lead to an ultimate place of safety (whether or not the exits are specifically designated as fire exits) | |
| Staircase Landing | BS 5839-1:2017 | 20.2 | MCPs should not be located on stairway landings, as persons travelling down the stairway might operate an MCP several floors below that on which a fire is located, resulting in evacuation of inappropriate areas. |
| Protecting Cover / Duct Proof | BS 5839-1:2025 | MCP may provide fitting covers or guards to prevent false alarms and damage. | |
| NFPA 72 | 17.14.7 | Listed protective covers shall be permitted to be installed over single- or double-action manually actuated alarm initiating devices. | |
| IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | Manual call points shall be housed in dust pre of and moisture proof enclosure properly sealed with rubber lining. | |
| Recess Mounting | IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | Where the call points are not visible from the front as in the case of a long corridor, they shall be surface mounted or semi-recessed in order to present a side profile area of not less than 750 mm. |
| BS 5839-1:2017 | 20.2 | MCPs may be flush-mounted in locations where they will be seen readily, but, where they will be viewed from the side (e.g. corridors), they should be surface mounted or only semi-recessed with the front face proud of the mounting surface by no less than 15 mm. | |
| MCP Glass Size & Thickness | IS 2189 | 6.3.8 | The glass surface shall be minimum 30 mm in area and glass thickness shall not exceed 2 mm. |
| MCP/ Pull Station | NFPA 72 | 17.14.6 | Manually actuated alarm-initiating devices shall be permitted to be single action or double action. |
| NBC 2016 | 6.4.2.2 | The manual call points shall be break glass and not pull stations. | |
| Color | NFPA 72 | 17.14.8.3 | Unless installed in an environment that precludes the use of red paint or red plastic, manual fire alarm boxes shall be Red in color. |






Recent Comments